Datei:Atmospheric Transmission.svg

Größe der PNG-Vorschau dieser SVG-Datei: 614 × 600 Pixel. Weitere aus SVG automatisch erzeugte PNG-Grafiken in verschiedenen Auflösungen: 246 × 240 Pixel | 491 × 480 Pixel | 786 × 768 Pixel | 1.048 × 1.024 Pixel | 2.096 × 2.048 Pixel | 741 × 724 Pixel
Originaldatei (SVG-Datei, Basisgröße: 741 × 724 Pixel, Dateigröße: 321 KB)
Dateiversionen
Klicke auf einen Zeitpunkt, um diese Version zu laden.
| Version vom | Vorschaubild | Maße | Benutzer | Kommentar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aktuell | 17:19, 18. Apr. 2023 |  | 741 × 724 (321 KB) | Efbrazil | Adding white background color so renders correctly on smartphone |
| 21:29, 7. Aug. 2022 |  | 741 × 724 (321 KB) | Efbrazil | color bug fix | |
| 21:00, 7. Aug. 2022 |  | 741 × 724 (321 KB) | Efbrazil | Fixed translations as best as possible using text editor for new layout | |
| 20:34, 7. Aug. 2022 |  | 741 × 724 (320 KB) | Efbrazil | Fixing text alignment | |
| 20:26, 7. Aug. 2022 |  | 741 × 724 (320 KB) | Efbrazil | Graphical improvements as per discussion page | |
| 18:59, 17. Feb. 2022 | 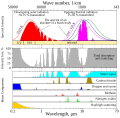 | 741 × 724 (208 KB) | Pierre cb | File uploaded using svgtranslate tool (https://svgtranslate.toolforge.org/). Added translation for fr. | |
| 23:10, 18. Mär. 2021 |  | 741 × 724 (180 KB) | Cepheiden | german labels adjusted | |
| 23:09, 18. Mär. 2021 |  | 741 × 724 (180 KB) | Cepheiden | correction of labels | |
| 23:06, 18. Mär. 2021 |  | 741 × 724 (180 KB) | Cepheiden | File uploaded using svgtranslate tool (https://svgtranslate.toolforge.org/). Added translation for de. | |
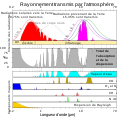
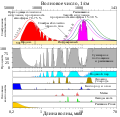
| 22:52, 18. Mär. 2021 |  | 741 × 724 (154 KB) | Cepheiden | =={{int:filedesc}}== {{Information |description= {{en|1=This figure shows the absorption bands in the Earth's atmosphere (middle panel) and the effect that this has on both solar radiation and upgoing thermal radiation (top panel). Individual absorption spectrum for major greenhouse gases plus Rayleigh scattering are shown in the lower panel.}} |date=2021-03-18 |source=This figure was prepared by Robert A. Rohde for the Global Warming Art project. |author=[[User:Д.Ил... |
Dateiverwendung
Die folgende Seite verwendet diese Datei:
Globale Dateiverwendung
Die nachfolgenden anderen Wikis verwenden diese Datei:
- Verwendung auf ar.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf el.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf en.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf fr.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf gl.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf ha.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf ig.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf pt.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf simple.wikipedia.org
- Verwendung auf zh.wikipedia.org