Aminodihydroindendicarbonsäure
chemische Verbindung
1-Amino-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1,5-dicarbonsäure oder AIDA ist ein fester, meist grober pulverförmiger Stoff mit charakteristischem Geruch aus der Stoffgruppe der Indanderivate.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
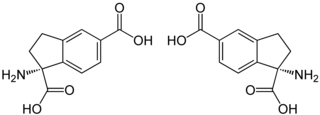
| |||||||||||||
| (R)-Form (links) und (S)-Form (rechts) | |||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||
| Name | Aminodihydroindendicarbonsäure (AIDA) | ||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C11H11NO4 | ||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
weißer Feststoff[1] | ||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 221,21 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | ||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit | |||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
BearbeitenAIDA kann aus Indan-carbaldehyden mit (R)-Prolin als Katalysator gewonnen werden.[2][3]
Verwendung
BearbeitenAIDA wird in der pharmakologischen Forschung verwendet. Das Einsatzgebiet beschränkt sich im Einsatz als selektiver Inhibitor für Subtyp 1 Metabotrope Glutamatrezeptoren.[4][5]
Einzelnachweise
Bearbeiten- ↑ a b c d Datenblatt AIDA bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 15. Juni 2011 (PDF).
- ↑ Jeff T. Suri, Derek D. Steiner, and Carlos F. Barbas, III: Organocatalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Ligands, Org. Lett., 2005, 7 (18), pp 3885–3888; doi:10.1021/ol0512942.
- ↑ Dawei Ma, Hongqi Tian, and Guixiang Zou: Asymmetric Strecker-Type Reaction of α-Aryl Ketones. Synthesis of (S)-αM4CPG, (S)-MPPG, (S)-AIDA, and (S)-APICA, the Antagonists of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors; J. Org. Chem., 1999, 64 (1), pp 120–125; doi:10.1021/jo981297a.
- ↑ Siniscalco D, Giordano C, Fuccio C, et al.: Involvement of subtype 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors in apoptosis and caspase-7 over-expression in spinal cord of neuropathic rats. In: Pharmacological Research. 57. Jahrgang, Nr. 3, März 2008, S. 223–233, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2008.01.007, PMID 18325779, PMC 2424141 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ Lee K, Boden PR: Characterization of the inward current induced by metabotropic glutamate receptor stimulation in rat ventromedial hypothalamic neurones. In: The Journal of Physiology. 504 ( Pt 3). Jahrgang, November 1997, S. 649–663, PMID 9401972, PMC 1159968 (freier Volltext).