Xenontrifluoridohexafluoroantimonat(V)
chemische Verbindung
Xenontrifluoridohexafluoroantimonat(V), XeF3[SbF6] ist eine chemische Verbindung zwischen dem Xenontrifluorid-Ion XeF3+ und der Hexafluorantimonsäure H[SbF6].
| Strukturformel | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
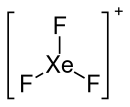 
| |||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||
| Name | Xenontrifluoridohexafluoroantimonat(V) | ||||||
| Summenformel | XeF3[SbF6] | ||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
gelbgrünliche Kristalle[1] | ||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||
| |||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||
| Molare Masse | 424,04 g·mol−1 | ||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | ||||||
| Dichte |
3,92 g·cm−3[1] | ||||||
| Schmelzpunkt |
110 °C[1] | ||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||
| |||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
BearbeitenDie Verbindung kann durch Lösung von Xenontetrafluorid XeF4 und Antimonpentafluorid SbF5 in Flusssäure HF gewonnen werden. Das Verhältnis der Lösung liegt bei 3,4:1.[3]
Eigenschaften
BearbeitenXenontrifluoridohexafluoroantimonat ist ein Feststoff, bestehend aus gelbgrünlichen Kristallen. Seine Dichte liegt bei 3,92 g·cm−3. Die Kristallstruktur der Verbindung ist monoklin.[3]
Literatur
Bearbeiten- R. J. Gillespie, B. Landa, G. J. Schrobilgen: Raman spectral studies of α- and β-trifluoroxenon hexafluoroantimonates, trifluoroxenon(1+) undecafluorodiantimonate(1-), trifluoroxenon(1+) hexafluoroarsenate(1-), trifluorooxoxenon(1+) hexafluoroantimonate(1-) and undecafluorodiantimonate(1-), and fluorodioxoxenon(1+) undecafluorodiantimonate(1-). In: Inorganic Chemistry. Juni 1976, S. 1256, doi:10.1021/ic50160a003.
- R. J. Gillespie, G. J. Schrobilgen: Trifluoroxenon(1+), trifluorooxoxenon(1+0), and fluorodioxoxenon(1+) cations. Preparation and characterization by fluorine-19 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In: Inorganic Chemistry. Oktober 1974, S. 2370, doi:10.1021/ic50140a015.
- D. E. McKee, C. J. Adams, Neil Bartlett: Preparation and Raman spectra of the salts [XeF3+][SbF6-], [XeF3+][Sb2F11-], [XeOF3+][SbF6-] and [XeOF3+][Sb2F11-]. In: Inorganic Chemistry. August 1973, S. 1722, doi:10.1021/ic50126a003.
Einzelnachweise
Bearbeiten- ↑ a b c David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 0-8493-0595-0, S. 4–94.
- ↑ Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- ↑ a b P. Boldrini, R. J. Gillepsie, P. R. Ireland, G. J. Schrobilgen: Crystal structure of trifluoroxenon(1+) hexafluoroantimonate(1-). In: Inorganic Chemistry. Juli 1974, S. 1690, doi:10.1021/ic50137a030.